入门
入门
# 入门
代码
配套的代码在 Github (opens new window) 中
# Vue.js 是什么
Vue 是一套用于构建用户界面的渐进式框架(可以只用 Vue,根据后续需要使用其他如 Router、Vuex 等)。
与其它大型框架不同的是,Vue 被设计为可以自底向上逐层应用。Vue 的核心库只关注视图层,不仅易于上手,还便于与第三方库或既有项目整合。另一方面,当与现代化的工具链以及各种支持类库结合使用时,Vue 也完全能够为复杂的单页应用提供驱动。
特点如下:
- 解耦视图和数据
- 可复用的组件
- 前端路由
- 状态管理
- 虚拟 DOM
# 安装
# CDN
对于制作原型或学习,你可以这样使用最新版本
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
对于生产环境,我们推荐链接到一个明确的版本号和构建文件,以避免新版本造成的不可预期的破坏
# npm
# CLI
# Vite
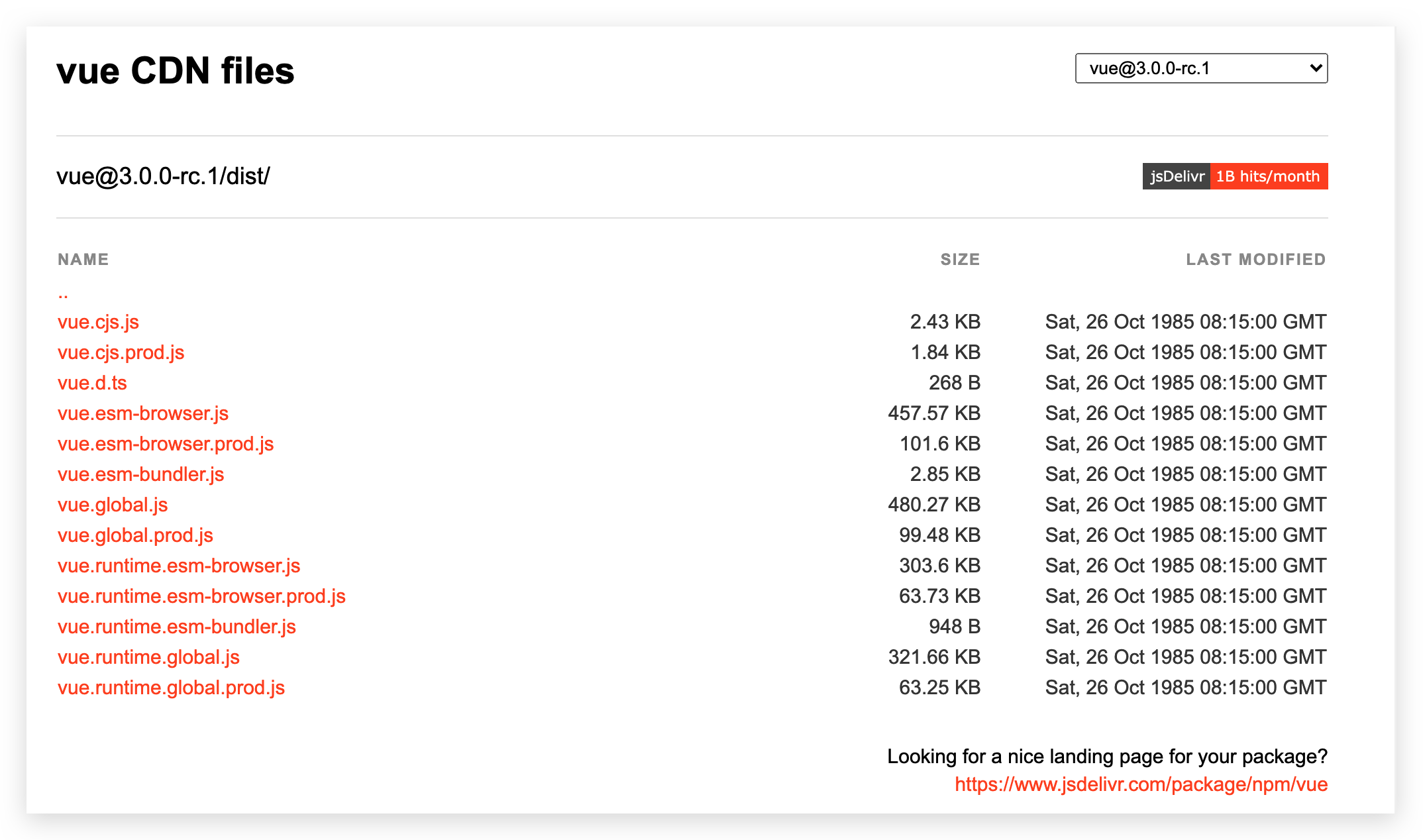
# 对不同构建版本的解释
在 npm 包的 dist/ 目录 (opens new window)你将会找到很多不同的 Vue.js 构建版本。这里列出了它们之间的差别:
# 计数器
可以将 template 中内容写到 html 中,Vue2 的 el 已被 mount() 替代:
# 写法1
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Hello World</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<script>
const options = {
// template中写么有提示,不方便。和#app不一样!,不能删掉#app
template: `
<button @click="decrement">-</button>
<span>{{counter}}</span>
<button @click="increment">+</button>
`,
data() {
return {
counter: 0,
}
},
methods: {
decrement() {
this.counter--
},
increment() {
this.counter++
},
},
}
// // Vue.createApp 创建 Vue 应用
// const app = Vue.createApp(options);
// // mount 装载到哪里,即在 id = root 的 html 中使用 vue
// const vm = app.mount('#root');
// 可以链式编程:
const vm = Vue.createApp(options).mount('#app')
</script>
</body>
</html>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
# 写法2
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Hello World</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<!-- 这种提示也不清晰 -->
<!-- <script type="x-template" id="temp">
<button @click="decrement">-</button>
<span>{{counter}}</span>
<button @click="increment">+</button>
</script> -->
<!-- 推荐 -->
<template id="temp">
<button @click="decrement">-</button>
<span>{{counter}}</span>
<button @click="increment">+</button>
</template>
<script>
const options = {
// 和#app不一样!,不能删掉#app
template: '#temp', //
data() {
return {
counter: 0,
}
},
methods: {
decrement() {
this.counter--
},
increment() {
this.counter++
},
},
}
// // Vue.createApp 创建 Vue 应用
// const app = Vue.createApp(options);
// // mount 装载到哪里,即在 id = root 的 html 中使用 vue
// const vm = app.mount('#root');
// 可以链式编程:
const vm = Vue.createApp(options).mount('#app')
</script>
</body>
</html>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
# 写法3
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Hello World</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<button @click="decrement">-</button>
<span>{{counter}}</span>
<button @click="increment">+</button>
</div>
<script>
const options = {
// 不写template也可以!
data() {
return {
counter: 0,
}
},
methods: {
decrement() {
this.counter--
},
increment() {
this.counter++
},
},
}
// // Vue.createApp 创建 Vue 应用
// const app = Vue.createApp(options);
// // mount 装载到哪里,即在 id = root 的 html 中使用 vue
// const vm = app.mount('#root');
// 可以链式编程:
const vm = Vue.createApp(options).mount('#app')
</script>
</body>
</html>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
# options
# template
表示的是Vue需要帮助我们渲染的模板信息。
- 它里面有很多的HTML标签,这些标签会替换掉我们挂载到的元素(比如id为app的div)的innerHTML;模板中有一些奇怪的语法,比如 {{}},比如 @click,这些都是模板特有的语法
- 如果字符串以
#开始,则它将被用作querySelector,并使用匹配元素的 innerHTML 作为模板字符串
有如下几种方式:
直接写template里面,有点过于别扭了,并且IDE很有可能没有任何提示,阻碍我们编程的效率。Vue还提供了两种方式:
使用script标签,并且标记它的类型为 x-template(和layui那种一样),设置id。
<script type="x-template" id="temp"></script> template: '#temp', //1
2
3注意和
mount('#app')不一样!template: '#temp'会把其内容渲染到 mount 中!使用任意标签(通常使用template标签,因为不会被浏览器渲染),设置id。🔥
<template id="temp"></template> template: '#temp', //1
2
3注意和
mount('#app')不一样!template: '#temp'会把其内容渲染到 mount 中!当然直接写在 mount 的元素中也可以!
# data
传入一个函数,并且该函数需要返回一个对象
- 在Vue2.x的时候,也可以传入一个对象(虽然官方推荐是一个函数)
- 在Vue3.x的时候,必须传入一个函数,否则就会直接在浏览器中报错
data 中返回的对象会被Vue的响应式系统劫持,之后对该对象的修改或者访问都会在劫持中被处理
- 所以我们在template中通过 访问counter,可以从对象中获取到数据
- 我们修改counter的值时,template中的 也会发生改变;
# methods
methods属性是一个对象,通常我们会在这个对象中定义很多的方法:
- 这些方法可以被绑定到 template 模板中;
- 在该方法中,我们可以使用this关键字来直接访问到data中返回的对象的属性
# this 绑定问题 🔥
methods 的方法定义为什么不能使用箭头函数(官方文档有给出解释)
不使用箭头函数的情况下,this到底指向的是什么? 是 window
箭头函数使用this的查找规则,它会在自己的上层作用于中来查找this,最终刚好找到的是script作用于中的this,所以就是window 🔥。
vue源码中使用 bind 绑定 publicThis 到每个 method 上,存入 ctx[methos]
# VSCode 代码片段 🔥
第一步,复制自己需要生成代码片段的代码;
第二步,https://snippet-generator.app/在该网站中生成代码片段;
第三步,在VSCode中配置代码片段;
# v-bind 🔥
- 一般使用:
v-bind:src='src'或简写:src='src'。只能传递单独的值 - 在封装高级组件时(底层是如Element的组件),可以使用
v-bind='info'来传递info对象!
# Todo-List 及组件初识
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Hello World</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<div>
<input v-model="item" />
<button @click="handleAddItem" :title="item">添加</button>
<ul>
<li v-for="(item,index) in list">
<todo-item
:item="item"
:index="index"
@handle-delete-item="handleDeleteItem"
/>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
<!-- 组件模版分离 -->
<template id="todo-item">
<span>{{index+1}}</span>
<span>--</span>
<span>{{item}}</span>
<button @click="handleDeleteItem(index)">删除</button>
</template>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script>
let options = {
data() {
return {
item: '',
list: [],
}
},
methods: {
handleAddItem() {
this.list.push(this.item)
this.item = ''
},
handleDeleteItem(index) {
this.list.splice(index, 1)
},
},
}
// Vue.createApp 创建 Vue 应用,存储到 app 中
//传入的参数表示,这个应用最外层的组件,该如何展示
const app = Vue.createApp(options)
// 组件
app.component('todo-item', {
template: `#todo-item`,
props: {
item: {
type: String,
default: '',
},
index: {
type: Number,
default: 0,
},
},
emits: ['handle-delete-item'],
methods: {
handleDeleteItem(index) {
this.$emit('handle-delete-item', index)
},
},
})
// mount 装载到哪里,即在 id = root 的 html 中使用 vue
// vm 就是 vue 应用的根组件
// mvvm 模式,m model 数据, v view 视图,vm viewModal视图数据连接层
const vm = app.mount('#root')
// 改变数据
// vm.$data.item = '测试课程'
// vm.item = '测试课程'
</script>
</body>
</html>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
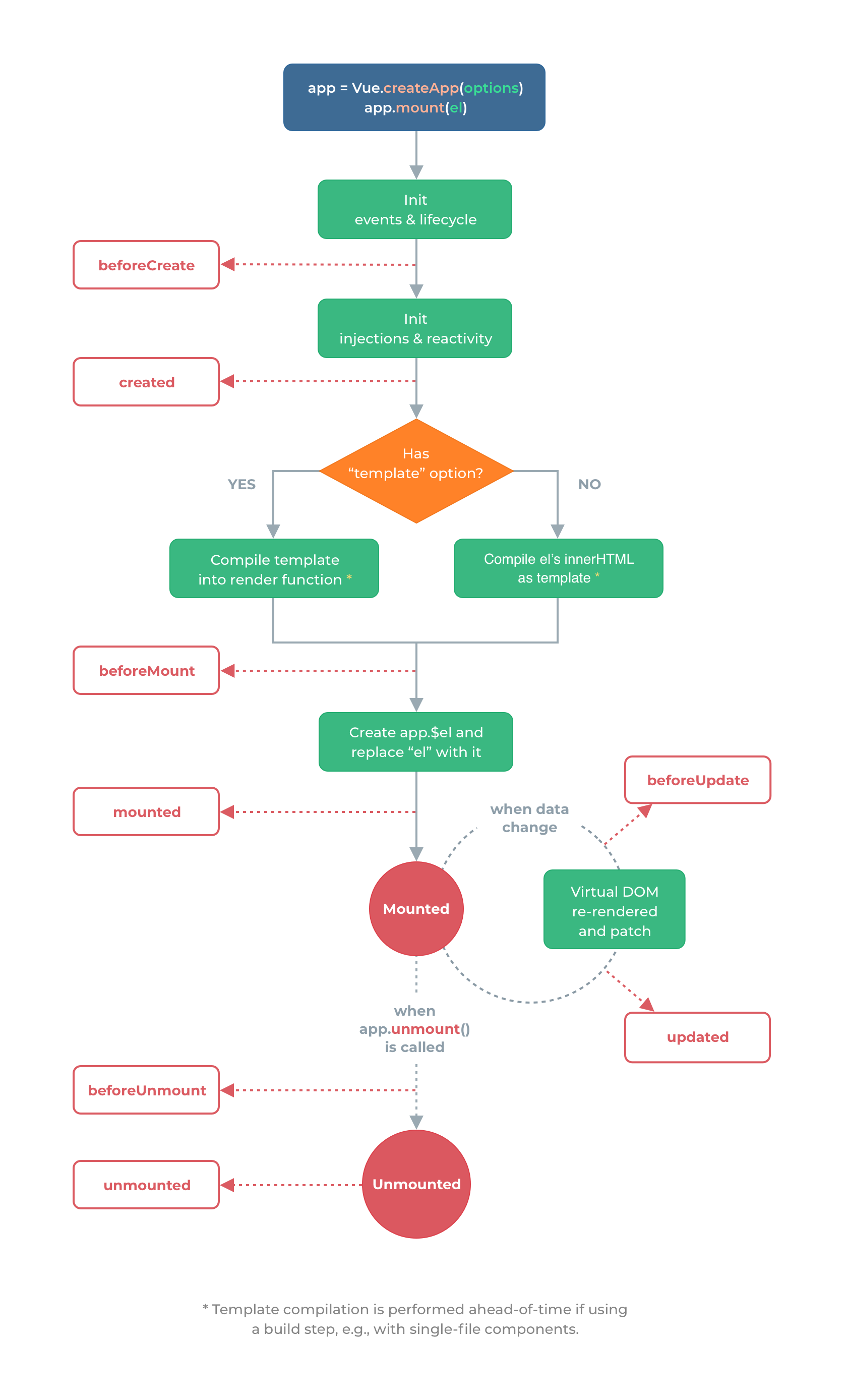
# 生命周期函数
注意 Vue2 的 destroy 等已被 unmount 等取代
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Hello World</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<div>{{counter}}</div>
</div>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
<script>
// 生命周期函数:在某一刻会自动执行的函数
// 执行完 Vue.createApp 并且 mount 后开始进行生命周期函数
let options = {
data() {
return {
counter: 1,
}
},
beforeCreate() {
console.log(
'=====[beforeCreate]: after init events & lifecycle。事件绑定、生命周期函数等。即 Vue 应用生成之前,Vue.createApp',
'。root innerHTML: ',
document.getElementById('root').innerHTML // 空
)
},
created() {
console.log(
'=====[created]: after init injections & reactivity。依赖注入、响应式(数据双向绑定)等。即 Vue 应用生成之后,Vue.createApp',
'。root innerHTML: ',
document.getElementById('root').innerHTML // 空
)
},
// 组件中有 template 则编译为 render 函数,没有则使用 mount 挂载的 el DOM 元素作为 template 进行编译
beforeMount() {
console.log(
'=====[beforeMount]: template(或 el) 的 innerHtml 被编译成render函数后。或称为组件被渲染到页面前。app.mount()',
'。root innerHTML: ',
document.getElementById('root').innerHTML // 空,此时没有任何内容!
)
},
mounted() {
console.log(
'=====[mounted]: after Create app.$el and replace "el" with it。 组件被渲染到页面后。此时页面的所有数据都可以正常展示!!!app.mount()',
'。root innerHTML: ',
document.getElementById('root').innerHTML // <div>1</div>
)
},
beforeUpdate() {
// 执行 vm.counter ++ 改变了 data 中数据即可
console.log(
'=====[beforeUpdate]: when data change, before Virtual DOM re-rendered and patch。即 data 变化,且页面重新渲染前执行',
'。root innerHTML: ',
document.getElementById('root').innerHTML // <div>1</div>
)
},
updated() {
// 执行 vm.counter ++ 改变了 data 中数据即可
console.log(
'=====[updated]: when data change, after Virtual DOM re-rendered and patch。即 data 变化,且页面重新渲染后执行',
'。root innerHTML: ',
document.getElementById('root').innerHTML // <div>2</div>
)
},
beforeUnmount() {
console.log(
'=====[beforeUnmount]: when app.unmount() is called。即 Vue 应用失效时,类比 beforeMount',
'。root innerHTML: ',
document.getElementById('root').innerHTML // <div>2</div>
)
},
unmounted() {
console.log(
'=====[unmounted]: when app.unmount() is called。即 Vue 应用失效,且 DOM 完全销毁之后,类比 mounted',
'。root innerHTML: ',
document.getElementById('root').innerHTML // 空
)
},
}
// Vue.createApp 创建 Vue 应用
// mount 装载到哪里,即在 id = root 的 html 中使用 vue
const app = Vue.createApp(options)
const vm = app.mount('#root')
// vm.$data.counter = 2
vm.counter = 2
// app.unmount()
</script>
</body>
</html>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97