 插槽
插槽
# 插槽 Slot
# 基本使用 & 默认内容
App.vue
<template>
<div>
<my-slot-cpn>
<!-- 注意,这里面会对 my-slot-cpn 中定义的 3 个插槽都写入 button-->
<button>我是按钮</button>
</my-slot-cpn>
<hr />
<!-- 注意,这里面会对 my-slot-cpn 中定义的 3 个插槽都写入 我是普通的文本-->
<my-slot-cpn> 我是普通的文本 </my-slot-cpn>
<hr />
<my-slot-cpn>
<!-- 注意,这里面会对 my-slot-cpn 中定义的 3 个插槽都写入 my-button 组件-->
<my-button />
</my-slot-cpn>
<hr />
<!-- 注意,这里面会对 my-slot-cpn 中定义的 3 个插槽启用默认值-->
<my-slot-cpn />
<hr />
<!-- 插入了很多的内容 -->
<my-slot-cpn>
<!-- 注意,这里面会对 my-slot-cpn 中定义的 3 个插槽分别!!!插入如下3个元素!!!总共出现9个!!!-->
<h2>哈哈哈</h2>
<button>我是按钮</button>
<strong>我是strong</strong>
</my-slot-cpn>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import MySlotCpn from './MySlotCpn.vue'
import MyButton from './MyButton.vue'
export default {
components: {
MySlotCpn,
MyButton,
},
}
</script>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
MySlotCpn.vue
<template>
<div>
<h2>组件开始</h2>
<slot>
<i>我是默认的i元素</i>
</slot>
<slot>
<i>我是默认的i元素</i>
</slot>
<slot>
<i>我是默认的i元素</i>
</slot>
<h2>组件结束</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
}
</script>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
MyButton.vue
<template>
<div>
<button>coderwhy button</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
}
</script>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# 具名插槽 🔥
v-slot:left可以简写为#left- 一个不带
name的slot,会带有隐含的名字 default - 动态插槽名:通过
v-slot:[dynamicSlotName]方式动态绑定一个名称
App.vue
<template>
<div>
<nav-bar :name="name">
<template #left>
<button>左边的按钮</button>
</template>
<template #center>
<h2>我是标题</h2>
</template>
<template #right>
<i>右边的i元素</i>
</template>
<template #[name]>
<i>why内容</i>
</template>
</nav-bar>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import NavBar from './NavBar.vue'
export default {
components: {
NavBar,
},
data() {
return {
name: 'why',
}
},
}
</script>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
NavBar.vue
<template>
<div class="nav-bar">
<!-- <slot name="default"></slot> -->
<div class="left">
<slot name="left"></slot>
</div>
<div class="center">
<slot name="center"></slot>
</div>
<div class="right">
<slot name="right"></slot>
</div>
<div class="addition">
<slot :name="name"></slot>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: {
name: String
}
// data() {
// return {
// name: "why"
// }
// }
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.nav-bar {
display: flex;
}
.left, .right, .center {
height: 44px;
}
.left, .right, .addition {
width: 80px;
background-color: red;
}
.center {
flex: 1;
background-color: blue;
}
</style>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
# 作用域插槽 🔥
# 渲染作用域 🔥
- 父级模板里的所有内容都是在父级作用域中编译的;
- 子模板里的所有内容都是在子作用域中编译的;
如何理解这句话呢?我们来看一个案例:
- 在我们的案例中ChildCpn自然是可以让问自己作用域中的title内容的;
- 但是在App中,是访问不了ChildCpn中的内容的,因为它们是跨作用域的访问;

# 作用域插槽 🔥
有时候我们希望插槽可以访问到子组件中的内容是非常重要的
- 当一个组件被用来渲染一个数组时,我们使用插槽,并且希望插槽中不要显示直接每项的内容,样式需通过父组件定义;
- 这个Vue给我们提供了作用域插槽;
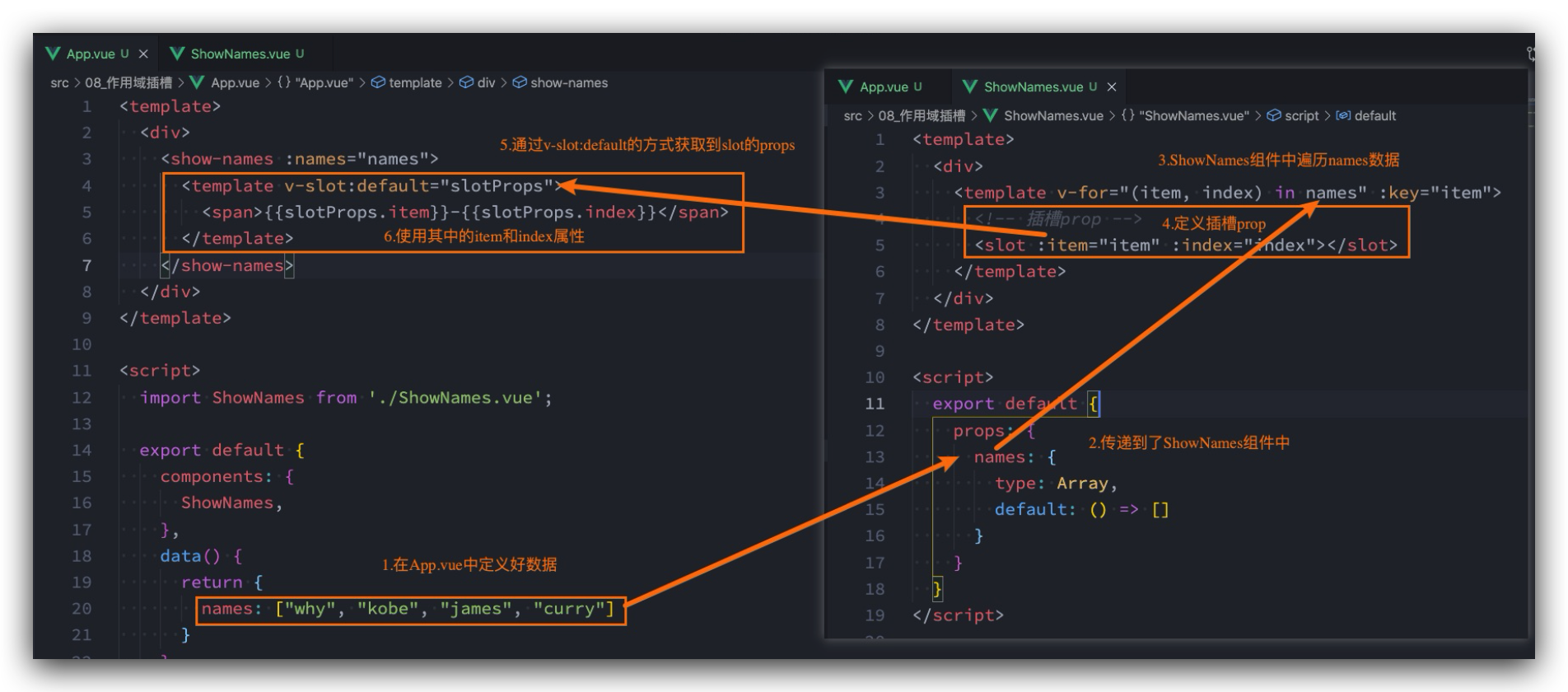
# 独占默认插槽的缩写
见示例
# 示例
App.vue
<template>
<div>
<show-names :names="names">
<template v-slot="coderwhy">
<button>{{ coderwhy.item }}-{{ coderwhy.index }}</button>
</template>
</show-names>
<!-- 独占默认default插槽,无需写template -->
<show-names :names="names" v-slot="coderwhy">
<button>{{ coderwhy.item }}-{{ coderwhy.index }}</button>
</show-names>
<!-- 注意: 如果还有其他的具名插槽, 那么默认插槽也必须使用template来编写 -->
<show-names :names="names">
<template v-slot="coderwhy">
<button>{{ coderwhy.item }}-{{ coderwhy.index }}</button>
</template>
<template v-slot:why>
<h2>我是why的插入内容</h2>
</template>
</show-names>
<show-names :names="names">
<template v-slot="slotProps">
<strong>{{ slotProps.item }}-{{ slotProps.index }}</strong>
</template>
</show-names>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import ChildCpn from './ChildCpn.vue'
import ShowNames from './ShowNames.vue'
export default {
components: {
ChildCpn,
ShowNames,
},
data() {
return {
names: ['why', 'kobe', 'james', 'curry'],
}
},
}
</script>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
ShowNames.vue
<template>
<div>
<template v-for="(item, index) in names" :key="item">
<slot :item="item" :index="index"></slot>
<slot name="why"></slot>
</template>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: {
names: {
type: Array,
default: () => []
}
}
}
</script>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
编辑 (opens new window)
上次更新: 2022/03/23, 17:55:39
